Despite the centre of numerous and bizarre conspiracy theories, Industry 4.0 merely represents a natural evolution in how we develop, produce and deliver products.
In this respect, it’s the fourth generation that has occurred in manufacturing, while it looks to optimise the digitisation of industry and manufacturing and build on the technologies introduced during Industry 3.0.
Such technologies have helped to unlock and improve processes such as simulation, which use models to mimic the operations of a particular system. Of course, aviation and the medical industry have been using simulation training since the 1960s, but modern technologies have proven success in transforming this practice throughout the various stages of industrial evolution.
But how will technology continue to revolutionise professional welder training, and what benefits will this create for the industrial services sector?
The Benefits of Tech on Professional Welder Training
The advent of Industry 4.0 has narrowed the focus on innovation and digitisation as key drivers of performance across a wide range of industries. So, rather than disrupting existing processes by introducing new technologies, it will help enhance the adoption of these technologies and unlock the tangible productivity increases and cost savings that businesses crave. At the same time, it can be argued that traditional welding remains inefficient, costly and polluting in the digital age.These include:
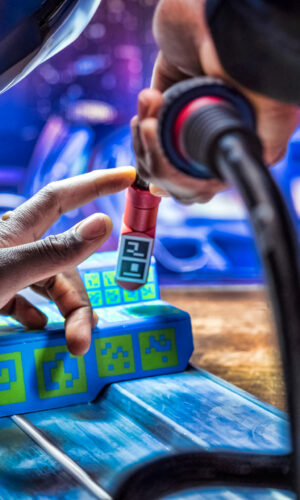
- Improved and High Quality Performance: Through Soldamatic’s solution, instructors can track each individual exercise and welder performance, contributing to personalised learning modules over time.
- Reduce Costs: This solution also drives an estimated cost reduction of 66% when compared with manual welding training. Unsurprisingly, these savings occur in the form of raw materials and consumables.
- Enhanced Efficiency: The combination of simulation and personalised learning observations translates into improved efficiency, with real practice time reduced by 32% when using Soldamatic’s solution.
- Optimal Safety: Simulated training of this type also eliminates the risk of injury, while simplifying the process of teaching correct posture to students. This ensures that the next generation of welders can minimise the risk of incurring long-term injury going forward.
- Driving Positive Environmental Impacts: By switching to a training simulation model, it’s thought that you can reduce CO2 emissions associated with welding by around 99%. This is significant, especially in an age of corporate social responsibility where businesses are increasingly focused on minimising their emissions.
The Soldamatic Industrial Services Model
As we can see, the Soldamatic industrial services model directly tackles the primary issues with manual welding training. It certainly improves general efficiency levels and reduces costs, while eliminating 99% of associated CO2 emissions. Long-term savings can also be unlocked through the effective teaching of safe usage and practices, by minimising the risk of long-term injuries and the financial impact of absenteeism. Welding accidents also comprise approximately 25% of fatal occupational accidents in the UK for example, so reducing this number can deliver positive financial and human impacts for businesses. If we also imagine the efficient nature of simulated welding training and its ability to create intuitive and bespoke learning programs (based on each welder’s individual performance), the process of upskilling trained professionals becomes more easier and more effective. This makes it far easier for manufacturers and industries to adapt to technological trends and changing demands, which is more important than ever in the age of Industry 4.0.
Accurate, sustainable, safe training relies on “virtual welding- based on augmented reality”
Soldamatic has been part of Regensburg’s vocational training program since 2021. Instructions and tips are displayed during the welding process; detailed analyses of the weld seam are possible afterwards. In addition to qualitative progress, the digitization project also contributes to the “green factory”: Compared to conventional learning welding, less metal scrap is produced. Electricity and material consumption are reduced. The significantly lower risk of injury is also among the positive effects. Only when sufficient basic knowledge has been acquired in the course of virtual welding do the trainees switch to the “real” welding machine.
Now that we understand the benefits of technology and how it can drive change in the world of professional welder training, it’s important to take a closer look at the Soldamatic industrial services model and its four distinct phrases. Here’s a breakdown:
- #1. Assessment: This process starts with a deep dive of a user’s bespoke needs, before recommended, tailored solutions are offered alongside an estimated ROI. Further visibility studies of potential solutions are carried out before creating a detailed scope of work, which will lead into project development and a final ROI calculation.
- #2. Development: The next phase sees the development of your bespoke training module, starting with the simulation parametrization and the creation of a beginning and end point. This establishes a framework for your training model and allows for custom solutions development, ensuring that you have a workable program that can deliver optimal benefits.
- #3. Implementation: At this stage, you can kickstart the implementation process, which sees the practical delivery of the solution and requires the teaching of designated trainers. This ensures that they’re able to use the software to its fullest and deliver bespoke learning solutions, while this phase will also see all training contents fully digitised.
- #4. Software as a Service (SaaS): The final phase involves a dedicated post-implementation service, which also includes ongoing maintenance and support. Another key element here is performance monitoring, in order to identify potential inefficiencies and drive continuous improvement. You may even add new joints and solutions to the program during this phase, depending on your feedback and analysis.
The Last Word
For more than a decade, welding academies across the globe have embraced simulation as part of their training programs.
What’s clear is that the observed and recorded benefits of this lend themselves to professional usage and the industrial services sector, creating tangible advantages for users in the age of Industry 4.0.
At the same time, modern simulation programs can also directly tackle the core inefficiencies and costs associated with manual learning, while accelerating processes such as upskilling and optimising the quality of workmanship.
Ultimately, new innovations and the sophistication of existing technologies as part of Industry 4.0 can have a huge bearing on professional welder training and deliver significant benefits to the industry services sector.
